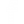Fact Friday

The ocean absorbs much of the excess carbon dioxide produced from the burning of fossil fuels. As the ocean absorbs this rampant increase in CO2, it reacts with sea water, changing the ocean’s chemistry. This process is called ocean acidification, and we are already seeing the negative impacts in our oceans. Here you can see the shell of the pteropod exposed to ocean acidification on the right is weaker and has visible damage, making it harder for the animal to survive.
Image credit: NOAA

February 21, 2025
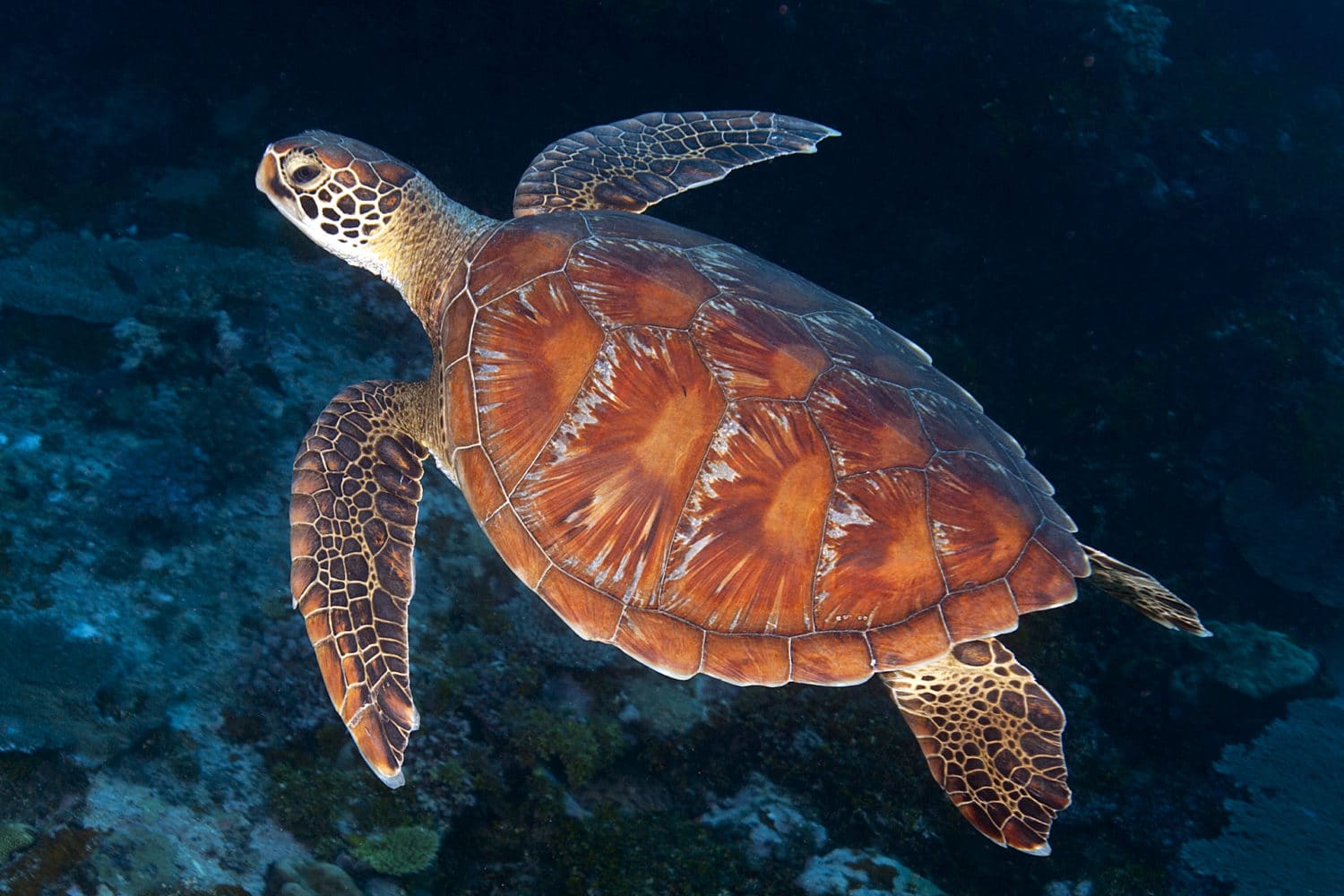
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles can hold their breath for 4-7 hours while sleeping and resting. How do they do it? Sea turtles are reptiles; like humans, they breathe air. They cannot breathe underwater. When a sea turtle is inactive, its metabolism and heartbeat “slows down,” which decreases the amount of oxygen it uses in its blood. Sea turtles can slow their heartbeat so that it only beats once every nine minutes! For comparison, the human heart beats an average of 80 times in one minute. One breath from the surface can go a long way for these amazing animals.
Photo Credit: Ken Marks